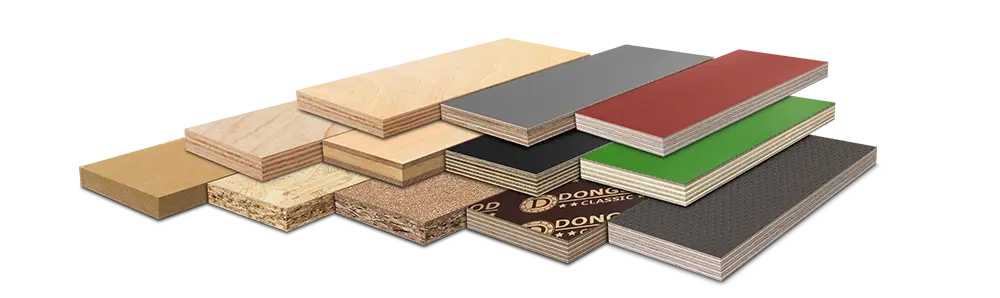
Plywood is a common type of board used in the construction industry, and different types of plywood are required for different uses.

1. Plywood is divided into three or more layers of thin wood and glued. Most of the thin wood produced now is spun thin wood, which is often called veneer. Odd numbered veneers are usually used. The fiber directions of adjacent veneers are perpendicular to each other. Three ply, five ply, seven ply and other odd numbered plywood are commonly used. The outermost veneer is called veneer, the front veneer is called panel, the reverse veneer is called back plate, and the inner veneer is called core plate or middle plate.
2. The species of plywood panel is the species of the plywood. In China, the commonly used broad-leaved trees are basswood, Fraxinus mandshurica, birch, poplar, elm, maple, color wood, Huangbo, maple, nanmu, Schima superba, and Chinese wolfberry. The commonly used coniferous trees are masson pine, Yunnan pine, larch, spruce, etc.
3. There are many classification methods for plywood, which can be classified according to tree species, such as hardwood plywood (birch plywood, tropical hardwood plywood, etc.) and coniferous plywood;
4. According to the purpose, it can be divided into ordinary plywood and special plywood. Ordinary plywood is the plywood suitable for a wide range of purposes, and special plywood is the plywood for special purposes;


5. According to the water resistance and durability of the adhesive layer, ordinary plywood can be divided into weather resistant plywood (class I plywood, with durability, boiling resistance or steam treatment, can be used outdoors), water-resistant plywood (class II plywood, can be soaked in cold water, or often soaked in hot water for a short time, but not resistant to boiling) Moisture resistant plywood (Class III plywood, which can withstand short-term cold water immersion and is suitable for indoor use) and non moisture resistant plywood (class IV plywood, which is used under normal indoor conditions and has certain bonding strength).
6. According to the structure of plywood, it can be divided into plywood, sandwich plywood and composite plywood. The sandwich plywood is the plywood with plate core, and the composite plywood is the plywood with plate core (or some layers) composed of materials other than solid wood or veneer. The two sides of the plate core usually have at least two layers of veneers with wood grain vertically arranged with each other.
7. According to surface processing, it can be divided into sanded plywood, scraped plywood, veneered plywood and pre veneered plywood. The sanded plywood is the plywood whose surface is sanded by the sander, the scraped plywood is the plywood whose surface is scraped by the scraper, and the veneered plywood is the veneer material such as decorative veneer, wood grain paper, impregnated paper, plastic, resin adhesive film or metal sheet, The pre finished plywood is the plywood that has been specially treated at the time of manufacture and does not need to be modified during use.
8. According to the shape of plywood, it can be divided into plane plywood and formed plywood. Formed plywood refers to the plywood that has been directly pressed into curved surface shape in the mold according to the requirements of the product, for special needs, such as wall protection board, corrugated plywood of the ceiling, backrest and back legs of the chair.
9. The common manufacturing method of plywood is the dry heat method, that is, after the dry veneer is coated with glue, it is placed in a hot press to be glued into plywood. The main processes include log scribing and cross sawing, wood segment heat treatment, wood segment centering and rotary cutting, veneer drying, veneer sizing, slab preparation, slab pre pressing, hot pressing, and a series of post-treatment.
The purpose of wood heat treatment is to soften the wood segments, increase the plasticity of the wood segments, facilitate the subsequent wood segments to be cut or planed, and improve the quality of veneer. Common methods of wood segment heat treatment include boiling, simultaneous heat treatment of water and air, and steam heat treatment.