Birch plywood, derived from the versatile Betula Alleghaniensis—commonly referred to as American birch, Quebec birch, Hard birch, Silver birch, or Swamp birch—is a premium material that has captured the attention of artisans and craftsmen. Its exceptional durability, fine grain, and versatility make it a top choice for furniture, cabinetry, and various construction projects.
1. Introduction to Birch Plywood
Birch plywood is a high-grade material renowned for its stability and aesthetic appeal. It consists of layers of thin birch veneers bonded together with strong adhesives, giving it a smooth surface and solid structure. Birch plywood has become synonymous with quality, often preferred over other types of plywood due to its resilience and uniform grain pattern.
Key Features:
Fine, even texture
Durable and strong
Resistant to warping
Smooth, paint-friendly surface
Originating from birch trees in colder climates such as North America and parts of Europe, birch plywood holds its own as a high-performance material suitable for a variety of projects.
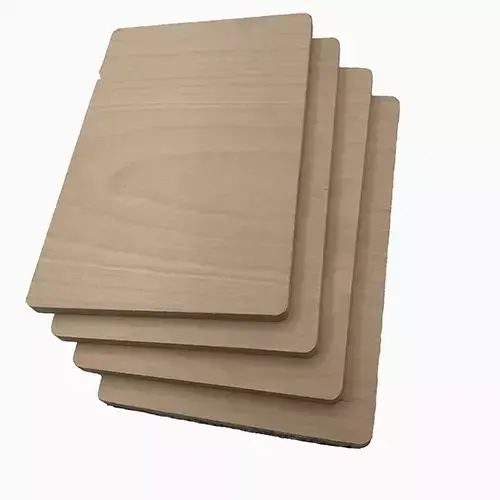

2. The Botanical Origins: Betula Alleghaniensis
The birch tree (Betula Alleghaniensis)—also known as yellow birch—is a remarkable species native to the northeastern United States and Canada. The hardwood from these trees is sought after for its flexibility and fine texture, making it ideal for plywood production.
Growing predominantly in cool, moist environments, the birch tree has a unique growth pattern, which contributes to the evenness of its grain. It is harvested sustainably, with forest management practices in place to ensure the species remains abundant.
3. Types of Birch Plywood
Though all birch plywood shares similar characteristics, various species have distinct properties, making them suited for different applications:
American Birch: Known for its toughness and light coloring, often used in cabinetry.
Quebec Birch: A dense variety from Canada, prized for its stability in high-moisture environments.
Hard Birch: Offers superior strength and is often used in industrial applications.
Silver Birch: More flexible, with a pale, fine grain, suitable for artistic projects.
Swamp Birch: Known for its water resistance, ideal for outdoor applications.
Understanding the differences in these types helps craftsmen choose the right material for their specific needs.

4. Birch Plywood Manufacturing Process
The process of creating birch plywood begins with carefully selecting and harvesting birch logs. The logs are debarked and peeled into thin layers known as veneers. These veneers are stacked in alternating grain directions and glued together under heat and pressure, which gives the plywood its strength.Key Manufacturing Steps:
Log Selection: Only the finest birch trees are chosen for high-grade plywood.
Veneer Production: Thin slices are carefully peeled from the log.
Layering and Pressing: Veneers are bonded in alternating directions to improve durability.
Finishing: The plywood is sanded for smoothness and graded based on visual quality.
This multi-step process ensures that birch plywood maintains its signature strength and appearance.