Melamine plywood and plastic laminates are common wooden products commonly used in the production of cabinets, furniture, etc. However, these two materials are slightly different. Plywood manufacturer China Fortuna has its own views on how to distinguish and use them:
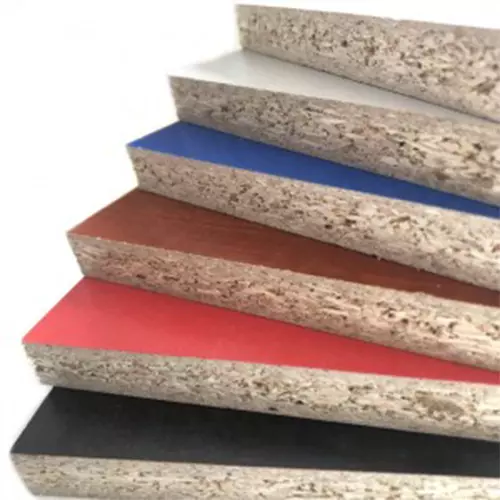


melamine board
Melamine is considered (commonly referred to as) direct or low-pressure laminates (LPL) because it is manufactured at pressures of 300-500 psi. The paper layer is soaked with melamine resin until it is melted and transformed into a solid plastic surface. Melamine board is molded into a layer of plastic laminated board, which is then bonded to particle board or other backing materials to form a durable plastic board that can be used to provide a beautiful surface for products such as Fomika.
Melamine board has a variety of textures and natural wood grain, making it an economically efficient and versatile choice to add color and finish to designs and projects. Melamine boards are usually glued onto particle boards for sale, making them durable, scratch resistant, shatterproof, and waterproof. Of course, although the material itself is waterproof, if water enters the particle board below, it will cause the melamine board to warp. In addition, although melamine board is very sturdy, improper installation may damage the particle board and cause it to shatter. Due to the gaps at both ends of the melamine board, edge sealing is required to cover the area. Projects built with melamine can typically last up to five years.


plastic laminate
Plastic laminates also come in various colors and textures, made from multi-layer kraft paper soaked in plastic resin and placed in a drying room. This material is a high-pressure laminate (HPL) with a pressure of 1400 pounds per square inch during manufacturing, which is more than three times that of melamine board. Plastic laminates have three levels: universal, vertical surface, and post formed, with the latter typically not bonded to wood.
Universal laminates are most commonly used on countertops. Vertical laminates are typically used for cabinets or other surfaces that do not directly wear out, while later formed laminates have plasticity and can be used for bending or curling applications. Although the cost of plastic laminates is slightly higher than that of melamine, they are more resistant to moisture, chemicals, heat, and have higher strength. Compared to using melamine for construction, using plastic laminates requires considerable skills and more specialized machinery.